User Guide
Where Got Time (WGT) a perfect desktop app dedicate to managing your events and plan out your meetings with your friends and family. It is developed for university student, who can type fast, to efficiently keep track of all of their events and their friends’ events via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, WGT can help you find a date that all your friends are free to meet instead of having to manually compare timetables with each other.
- Quick start
- Features
- General commands
- Person-related commands
- Group-related commands
- Event-related commands
- Data-related commands
- FAQ
- Command summary
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
wheregottime.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to an empty folder that you want to use as the home folder for your WhereGotTime. (e.g.: A new folder in your
Desktop) - On Windows, you can click the
wheregottime.jarfile to run the application: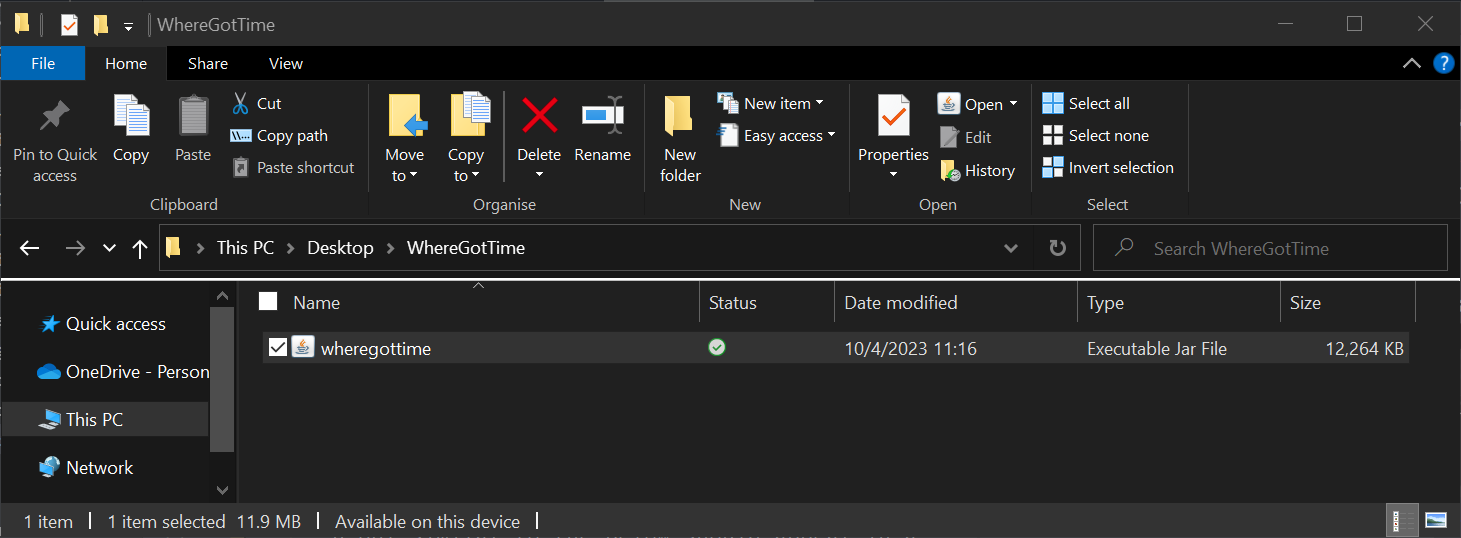
- Alternatively, open a command terminal:
-
On Windows: Click the file path bar and type
cmdand press theEnterbutton to start the command prompt: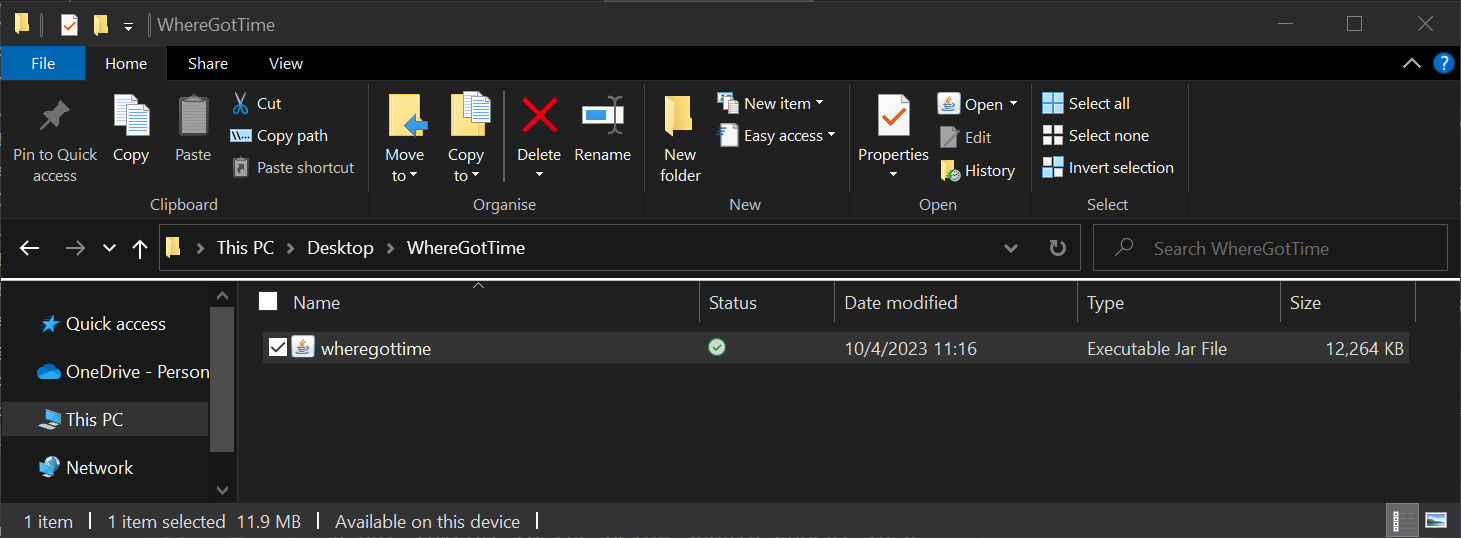 A window similar to the one below should appear:
A window similar to the one below should appear:
 Run the command
Run the command java -jar wheregottime.jarto start the application: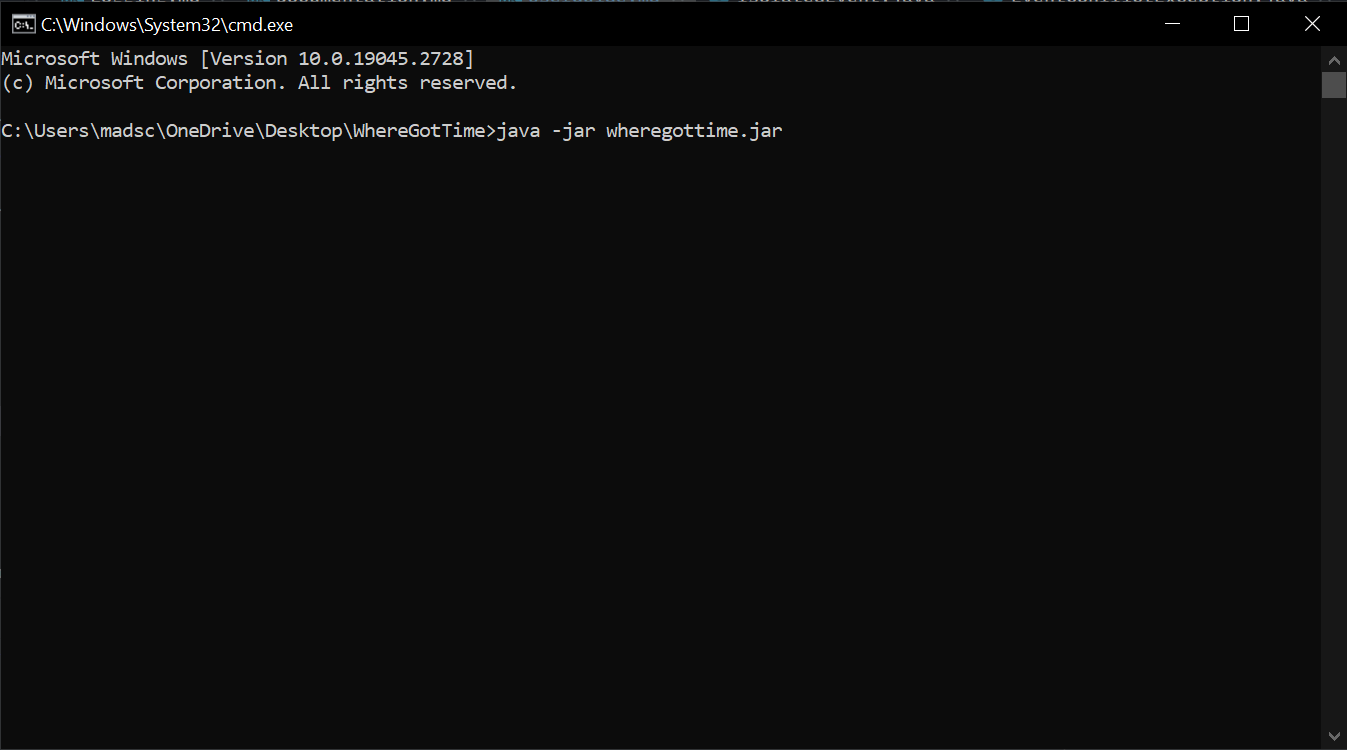
-
On Macs: Control-click on the home folder and click on
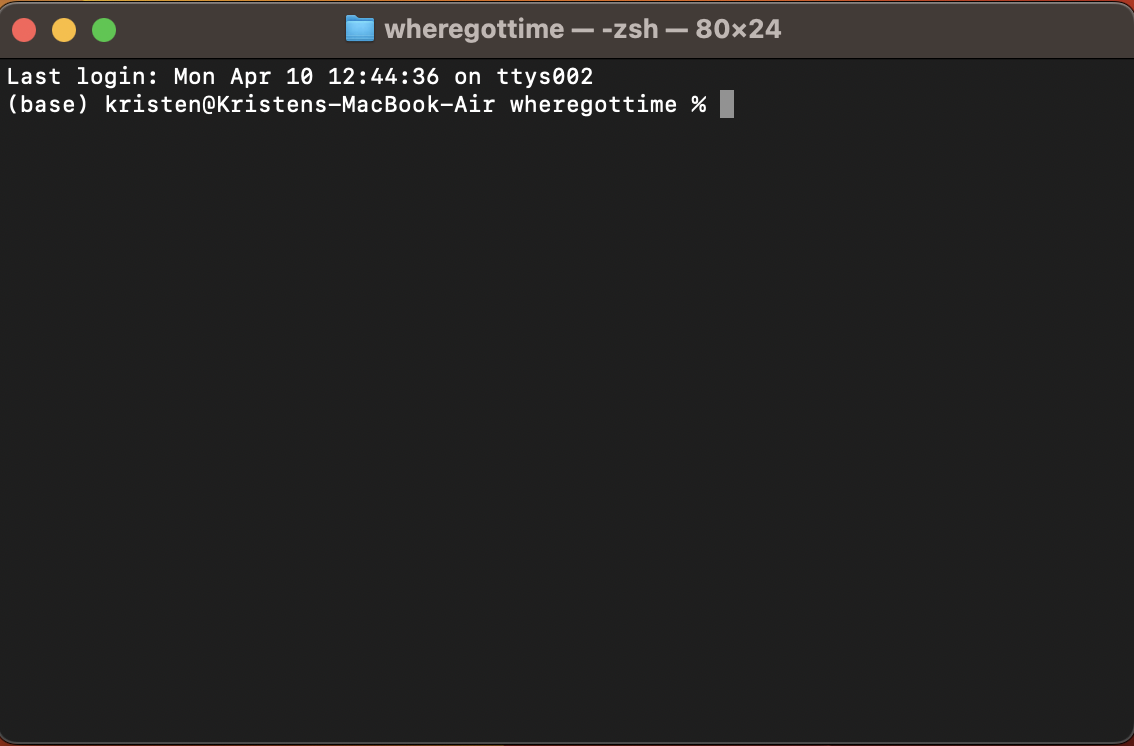
New Terminal at Folder</br> Note: Do not double click on the jar file as the app may not work as intended.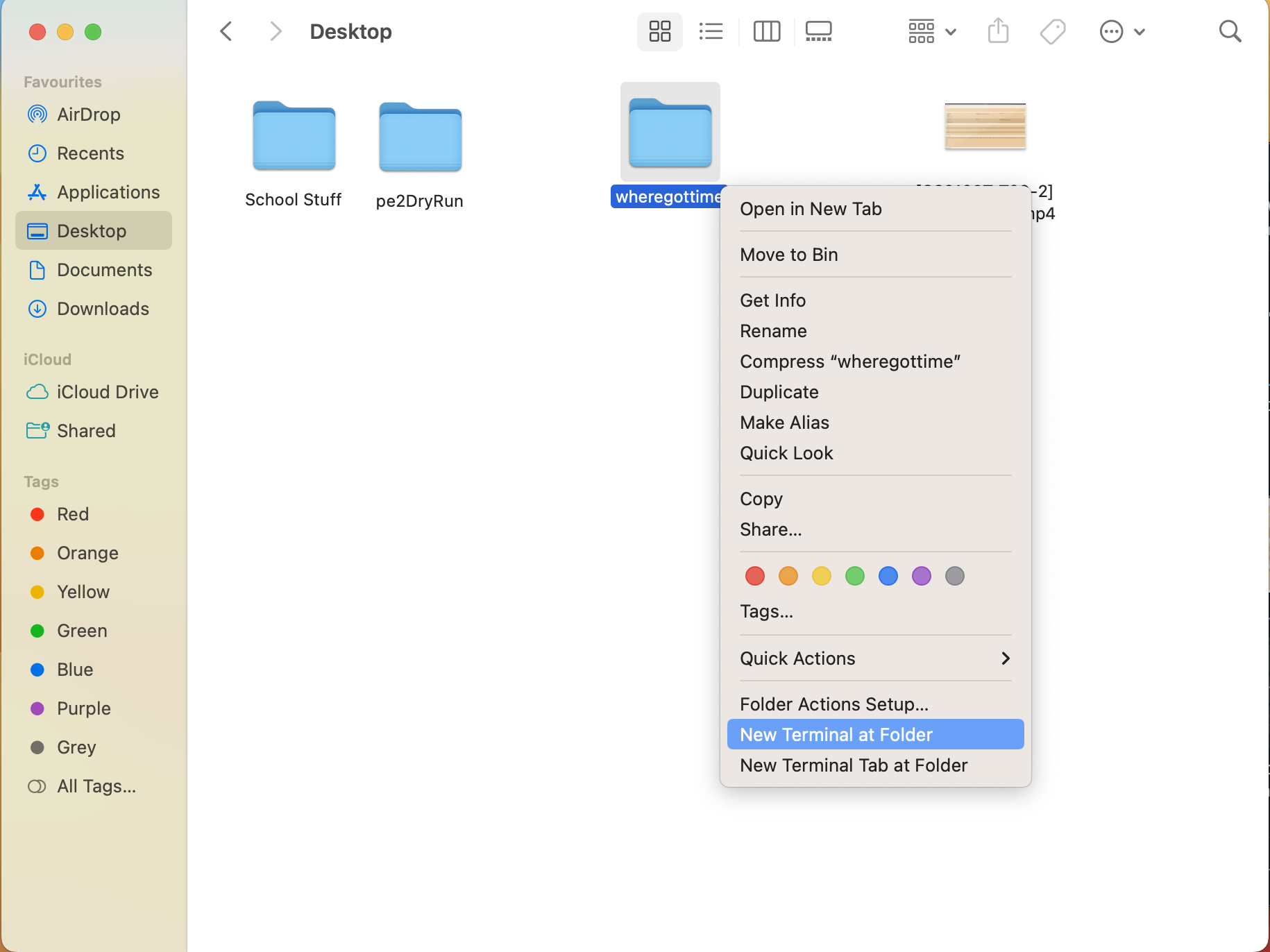 A window similar to the one below should appear:
A window similar to the one below should appear:
 Run the command
Run the command java -jar wheregottime.jarto start the application: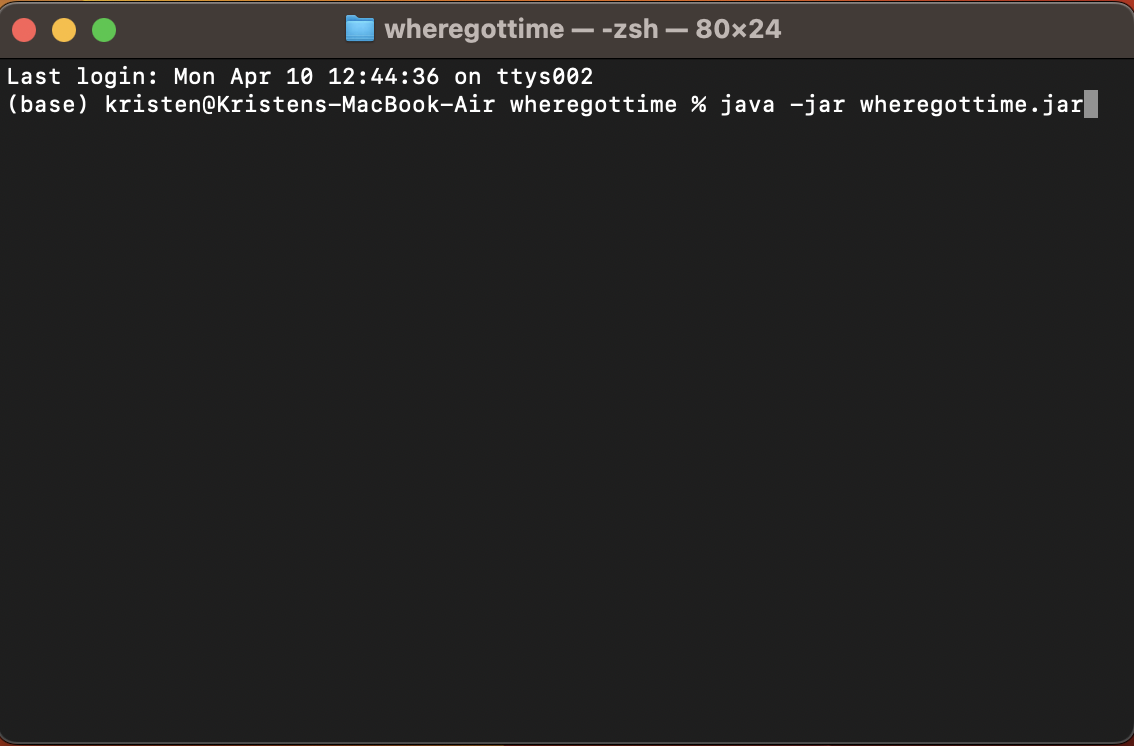
-
-
A GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
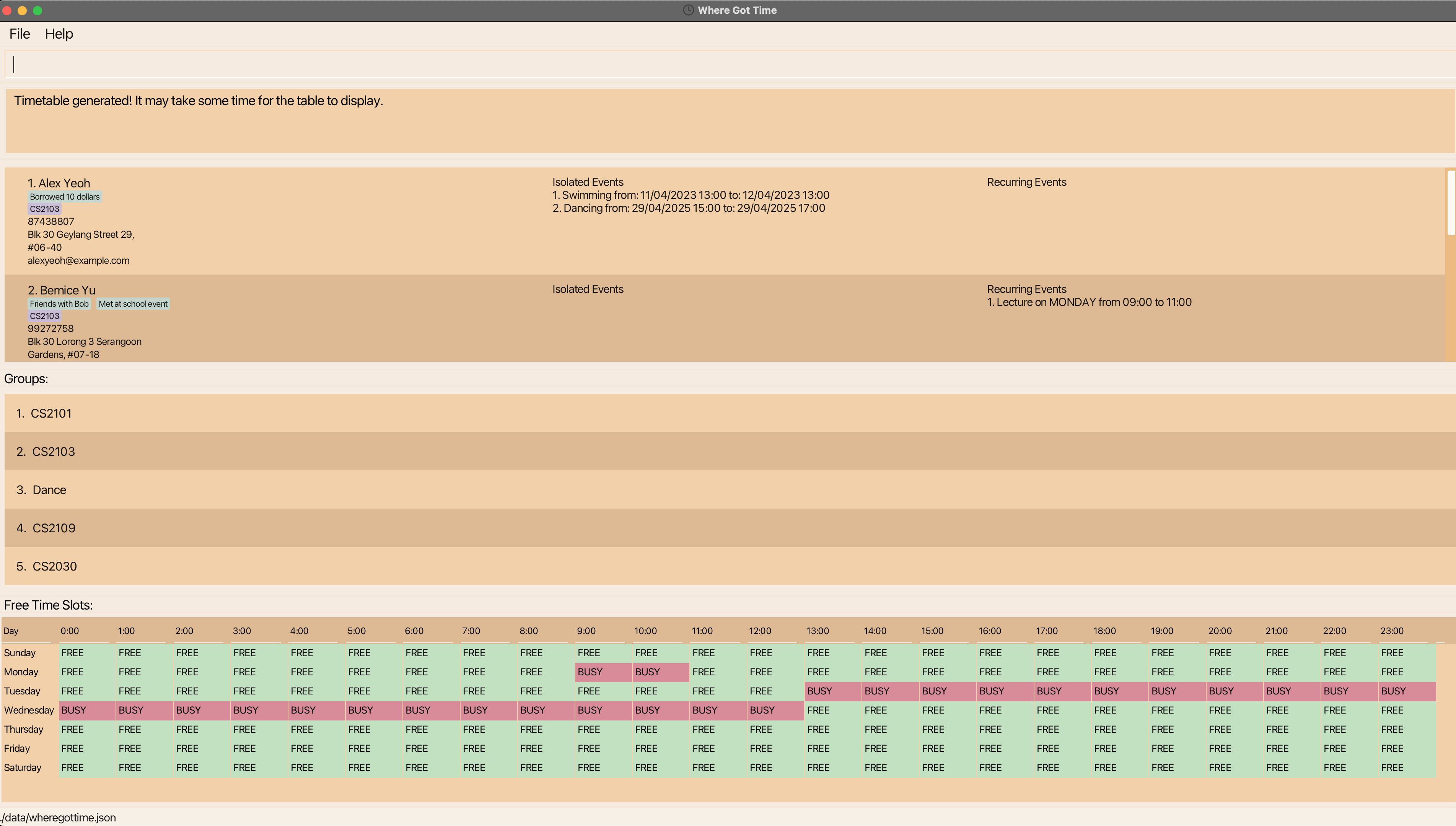
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list: Lists all contacts. -
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book. -
delete 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list. -
clear: Deletes all contacts. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
WARNING: Directly editing the saved json file may cause the app to malfunction
Demo video for the features.
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times (Even not at all).
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is specified multiple times when it is only expected once, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/12341234 p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp. -
For commands that require index, the index is based on the current person/group list shown.
General commands
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaning how to access the help page.
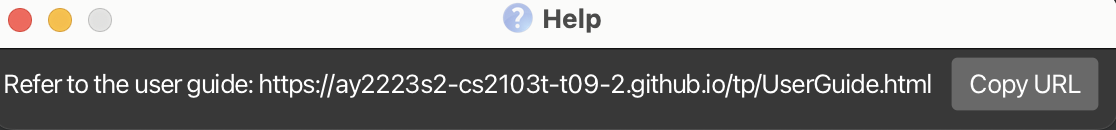
Format: help
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Person-related commands
Adding a person: add
Adds a person to the address book.
Format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG] [g/GROUP]…
- A person can only be added to an existing group
- Tags can only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces
Examples:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01add n/Betsy Crowe t/study buddy e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
Listing all persons : list
Shows a list of all persons in the address book.
Format: list
Editing a person : edit
Edits an existing person in the address book.
Format: edit INDEX [m/] [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] [g/GROUP]…
- Edits the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields (e.g.
NAME,PHONEetc.) must be provided. - Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags/groups, the existing tags/groups of the person will be removed i.e adding of tags/groups is not cumulative.
- To add on to existing groups/tags without overwriting it, include the prefix
m/(merge). - When using prefix
m/, groups/tags added cannot be empty. - Groups can only be added if they have been created.
- You can remove all the person’s tags/groups by typing
t/andg/respectively without specifying any tags/groups after it. - Adding duplicate groups/tags to a
Personwould not result in multiple groups/tags created.
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/ g/Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags and groups. -
edit 3 m/ t/Borrowed 10 dollarsEdit the tags of the 3rd person to beBorrowed 10 dollarsplus the existing tag of that person. -
edit 3 m/ g/CS2103TEdit the groups of the 3rd person to beCS2103Tplus the existing groups of that person.
Locating persons by name: find
Finds persons whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Persons matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
find JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li

Deleting a person : delete
Deletes the specified person from the address book.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the person at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd person in the address book. -
find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
Group-related commands
Creating a group : group_create
Create a group in the address book.
Format: group_create g/GROUP_NAME
- Creates a group with the specified group name
GROUP_NAME - The group name cannot be empty and can only contain alphanumeric characters!
- Only one group can be created at a time
- If more than one group is specified, only the last occurrence of a group will be taken
Examples:
group_create g/CS2103Tgroup_create g/CS2101
Deleting a group : group_delete
Deletes an existing group from the address book.
Format: group_delete GROUP_INDEX
- Deletes a group with the specified
GROUP_INDEX - The group index cannot be empty and must be an existing group
- Deleting a group will remove all persons in that group
Examples:
group_delete 1group_delete 2
List all groups: group_list
Shows a list of all existing groups’ name in the address book.
Format: group_list
Find a group: group_find
Finds persons in groups whose group names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: group_find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
CS2103will matchcs2103 - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
CS2103 CS2101will matchCS2101 CS2103 - Only the group name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
CS2103will not matchCS2103T - Persons with groups matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.CS2103 CS2101will return persons inCS2101,CS2103 - The group name cannot be empty
Examples:
-
group_find CS2103returns persons in the groupCS2103 -
group_find CS2103 CS2101returns persons in the groupCS2103andCS2101
Event-related commands
Creating an event:
Create events and add it to a specific person in WGT. WGT supports two types of events:
- Isolated events: one off events
- Recurring events: weekly events such as tutorials and lectures
Note that only hourly events can be created.
Note You will not be able to create an isolated event or recurring event if there is existing event happening in the same time period.
For example, 17:00 is a valid timing and 17:30 is an invalid timing
1) Isolated event: event_create
Format: event_create INDEX ie/EVENT_NAME f/START_DATETIME t/END_DATETIME
-
INDEXrefers to the index of the person to add the given isolated event - Creates an event with the specified name
EVENT_NAMEusing the flagie/which represents the words Isolated event - The flags
f/represent the word from andt/represents the word to -
EVENT_NAME,START_DATETIMEandEND_DATETIMEcannot be left empty -
If there are duplicate attributes (i.e.
event_create INDEX ie/test ie/test2 f/START_DATETIME t/END_DATETIME), WGT will take the info following the latest attribute (in the example case, WGT will take event name to be test 2). - The format of both
START_DATETIMEandEND_DATETIMEwould be indd/MM/yyyy HH:mm -
START_DATETIMEhas to be before theEND_DATETIME -
START_DATETIMEandEND_DATETIMEhas to be after the current date and time
Examples:
event_create 1 ie/CS2101 Presentation f/02/02/2025 16:00 t/28/02/2025 18:00
2) Weekly Recurring Event event_create_recur
Format: event_create_recur INDEX re/EVENT_NAME d/DAY_OF_WEEK f/START_TIME t/END_TIME
-
INDEXrefers to the index of the person whose recurring event list will be added with the given recurring event - Creates a recurring event with the specified name
EVENT_NAMEusing the flagrewhich represents the words Recurring event - The flag
d/represents the day of the week - The remaining flags
f/represent the word from andt/represents the word to - The format
DAY_OF_WEEKaccepts the inputMonday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday and Sunday - The format of
START_TIMEandEND_TIMEwould be inHH:mm -
EVENT_NAME,DAY_OF_WEEK,START_TIMEandEND_TIMEcannot be left empty
Examples:
event_create_recur 1 re/CS2103T Weekly Meeting d/Monday f/12:00 t/14:00event_create_recur 1 re/CS2103T Lecture d/Friday f/16:00 t/18:00
00:00 to 00:00 is not allowed. The maximum time period that is allowed is from 00:00 to 23:00.
Deleting an event:
Delete either an isolated or a weekly recurring event
1) Delete an isolated event: ie_delete
Deletes an existing isolated event from a person’s isolated event list in WGT.
Format: ie_delete PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX
- Deletes an event with the specified event index
EVENT_INDEXfrom the specified person with person indexPERSON_INDEX - Both
PERSON_INDEXandEVENT_INDEXand cannot be empty and must be an existing and valid person and index i.e. if there is only 3 persons stored in WGT, 4 is an invalidPERSON_INDEX
Examples:
ie_delete 1 1
2) Delete recurring event: re_delete
Deletes a recurring event from a person’s recurring event list in WGT.
Format: re_delete PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX
- Deletes an event with the specified event index
EVENT_INDEXfrom the specified person indexPERSON_INDEX - Both
PERSON_INDEXandEVENT_INDEXand cannot be empty and must be an existing person and index
Examples:
re_delete 1 1
Editing an event:
Edit the attributes of either an isolated event or a weekly recurring event
Note You will not be able to edit an isolated event or recurring event time period if there is existing event happening in the particular time period.
1) Edit an isolated event: ie_edit
Edit an existing isolated event from person’s isolated event list in WGT.
Format: ie_edit PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX [ie/NAME] [f/START_DATETIME] [t/END_DATETIME]
- Edit a weekly recurring event with the specified
EVENT_INDEXthat belong to a person with a specifiedPERSON_INDEX -
At least one attribute from isolated event must be included. The attributes are
[ie/NAME],[f/START_DATETIME]and[t/END_DATETIME] - Any attributes being edited on must be valid
-
NAMEmust only be in alphabetic or numeric terms -
START_DATETIMEandEND_DATETIMEmust be in the format ofdd/MM/yyyy HH:mm -
START_DATETIMEhas to be before theEND_DATETIME -
START_DATETIMEandEND_DATETIMEhas to be after the current date time
Examples:
ie_edit 1 1 ie/Bikingie_edit 1 1 f/09/03/2024 15:00
2) Edit a recurring event: re_edit
Edit an existing recurring event from person’s recurring event list in the address book.
Format: re_edit PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX [re/NAME] [d/DAY_OF_WEEK] [f/START_TIME] [t/END_TIME]
- Edit a weekly recurring event with the specified
EVENT_INDEXthat belong to a person with a specifiedPERSON_INDEX - At least one attribute from recurring event must be included. The attributes are
[re/NAME],[d/DAY_OF_WEEK],[f/START_TIME]and[t/END_TIME] - Any attributes being edited on must be valid
-
NAMEmust only be in alphabetic or numeric terms -
DAY_OF_WEEKmust be eitherMonday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday or Sunday -
START_TIMEandEND_TIMEmust be in the format ofHH:mm
Examples:
re_edit 1 1 re/Swimmingre_edit 1 1 d/Tuesdayre_edit 1 1 t/14:00
Find free time slots: free
Displays the time slots in a week when all members of the specified group are free (no events).
Format: free GROUP_INDEX [f/START_DATE]
- Finds unoccupied time slots within members of the group at the specified
GROUP_INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed group list. The index must be a positive 1, 2, 3 … - The
START_DATEfield is optional. The time slots will be shown for the week ahead, starting from that date. If it is not provided, then the current date will be used. -
START_DATEmust be of the format:dd/MM/yyyy - Note that if there are any changes to a person’s event(s), the time table will only be updated upon entering the
freecommand.
Example:
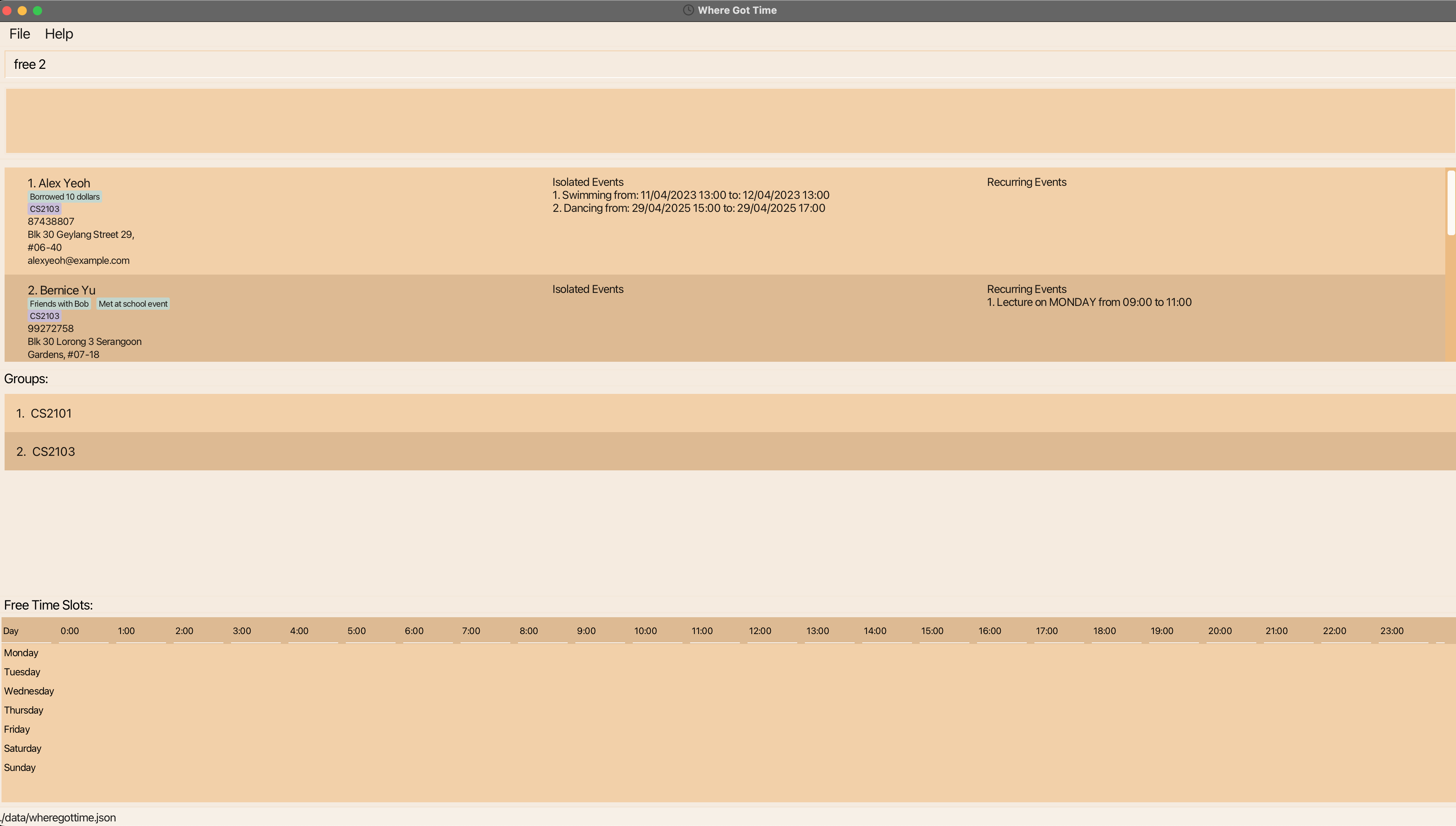 1) Let’s say you want to find a free time slot within the group ‘CS2103’.
2) Type the command
1) Let’s say you want to find a free time slot within the group ‘CS2103’.
2) Type the command free followed by the group index. In this case, the group index is 2.
3) Hit enter.
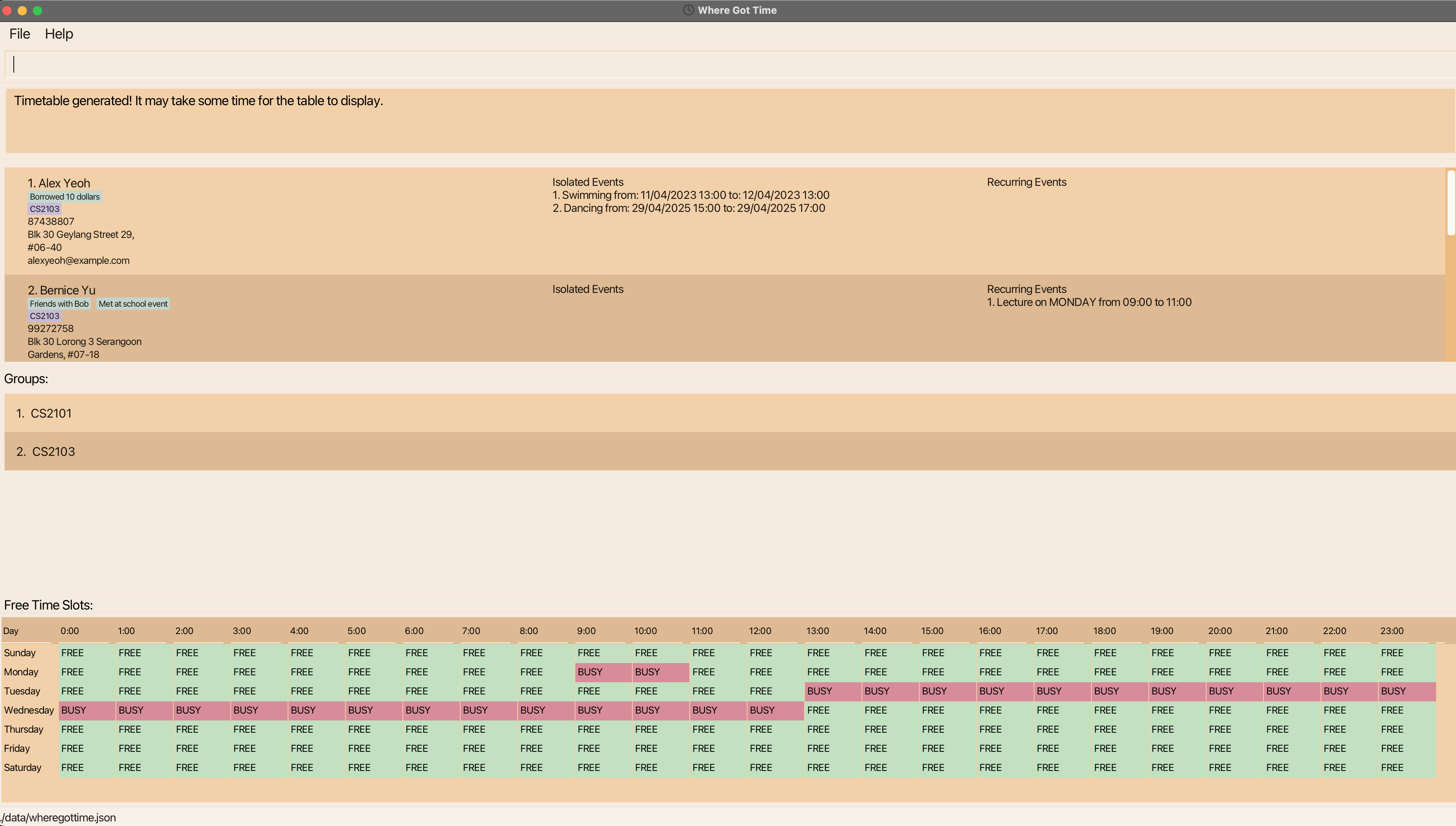 1) The free time slots will be generated and shown below.
2) The free time slots are shown from the current day that the command is entered.
3) However, if you would like to change the start date, you can indicate the
1) The free time slots will be generated and shown below.
2) The free time slots are shown from the current day that the command is entered.
3) However, if you would like to change the start date, you can indicate the START_DATE but it is optional.
Data-related commands
Importing data : import
Import one person into your address book to update their details and events.
Format: import
- Stored data must be in a file called
export.jsonand the file must be placed in the folderdatawhich is in the same location as the JAR file. - Stored data can only contain 1 person.
- The imported person will not have any tags or groups.
- This is because groups and tags are dependent on how the user wants to assign them. Therefore, merging or overwriting groups/tags when importing is not appropriate.
- If the imported person is already an entry in your address book with the same name (case-sensitive), their phone number, address, email as well as their event lists will be updated to the imported data.
- If the imported person is not yet an entry in your address book, a new entry will be created with the imported person’s details (excluding tags and groups).
Export a person: export
Export a person’s details from the address book.
Format: export [PERSON_INDEX]
- Exports a person’s details with the specified
INDEX - All details except groups and tags are exported (Reason mentioned in
Importsection) - Export data is saved in the data/export.json
- Exporting a person will overwrite any existing export.json file
Examples:
export 1export 2
Saving the data
WhereGotTime data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
WhereGotTime data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/wheregottime.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous WhereGotTime home folder.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| Add |
add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g., add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
|
|
| Clear | clear |
|
| Delete |
delete INDEXe.g., delete 3
|
|
| Edit |
edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] [g/GROUP]…e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com t/CS2103T g/e.g., edit 3 m/ t/CS2103T
|
|
| Find |
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find James Jake
|
|
| List | list |
|
| Help | help |
|
| Group create | group_create g/GROUP_NAME |
|
| Group delete | group_delete GROUP_INDEX |
|
| Group list | group_list |
|
| Group find |
group_find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] e.g., group_find CS2103 CS2101
|
|
| Isolated Event create | event_create INDEX ie/EVENT_NAME f/START_DATETIME t/END_DATETIME |
|
| Isolated Event delete | ie_delete PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX |
|
| Isolated Event update | ie_edit PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX [ie/NAME] [f/START_DATETIME] [t/END_DATETIME] |
|
| Recurring Event create | event_create_recur INDEX re/EVENT_NAME d/DAY_OF_WEEK f/START_TIME t/END_TIME |
|
| Recurring Event delete | re_delete PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX |
|
| Recurring Event update | re_edit PERSON_INDEX EVENT_INDEX [re/NAME] [d/DAY_OF_WEEK] [f/START_TIME] [t/END_TIME] |
|
| Export person | export [PERSON_INDEX] |
|
| Free | free GROUP_INDEX [f/START_DATE] |